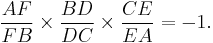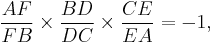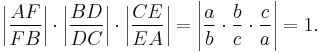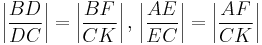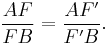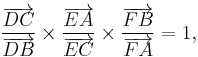Menelaus' theorem
Menelaus' theorem, named for Menelaus of Alexandria, is a theorem about triangles in plane geometry. Given a triangle ABC, and a transversal line that crosses BC, AC and AB at points D, E and F respectively, with D, E, and F distinct from A, B and C, then
This equation uses signed lengths of segments, in other words the length AB is taken to be positive or negative according to whether A is to the left or right of B in some fixed orientation of the line. For example, AF/FB is defined as having positive value when F is between A and B and negative otherwise.
The converse is also true: If points D, E and F are chosen on BC, AC and AB respectively so that
then D, E and F are collinear. The converse is often included as part of the theorem.
The theorem is very similar to Ceva's theorem in that their equations differ only in sign.
Contents |
Proof
A standard proof is as follows:[1]
First, the sign of the left-hand side negative since either all three of the ratios are negative, the case where the line DEF misses the triangle (lower diagram), or one is negative and the other two are positive, the case where DEF crosses two sides of the triangle. (See Pasch's axiom.)
To check the magnitude, construct perpendiculars from A, B, and C to the line DEF and let the lengths be a, b, and c respectively. Then by similar triangles it follows that |AF/FB| = |a/b|, |BD/DC| = |b/c|, and |CE/EA| = c/a. So
For a simpler, if less symmetrical way to check the magnitude,[2] draw CK parallel to AB where DEF meets CK at K. Then by similar triangles
and the result follows by eliminating CK from these equations.
The converse follows as a corollary.[3] Let D, E and F be given on the lines BC, AC and AB so that the equation holds. Let F′ be the point where DE crosses AB. Then by the theorem, the equation also holds for D, E and F′. Comparing the two,
But at most one point can cut a segment in a given ratio so F=F′.
A non-computational proof using homothecies
The following proof[4] uses only notions of affine geometry, notably homothecies. Whether or not D, E, F are collinear, there are three homothecies with centers D, E, F that respectively send B to C, C to A, and A to B. The composition of the three then is an element of the group of homothecy-translations that fixes B, so it is a homothecy with center B, possibly with ratio 1 (in which case it is the identity). This composition fixes the line DE if and only if F is collinear with D and E (since the first two homothecies certainly fix DE, and the third does so only if F lies on DE). Therefore D, E, F are collinear if and only if this composition is the identity, which means that the product of the three ratios is 1:
which is equivalent to the given equation.
History
It is uncertain who actually discovered the theorem, however the oldest extant exposition appears in Spherics by Menelaus. In this book, the plane version of the theorem is used as a lemma to prove a spherical version of the theorem.[5]
In Almagest, Ptolemy applies the theorem on a number of problems in spherical astronomy.[6] During the Islamic Golden Age, Muslim scholars devoted a number of works that engaged in the study of Menelaus' theorem, which they referred to as "the proposition on the secants" (shakl al-qatta'). The complete quadrilateral was called the "figure of secants" in their terminology.[6] Al-Biruni's work, The Keys of Astronomy, lists a number of those works, which can be classified into studies as part of commentaries on Ptolemy's Almagest as in the works of al-Nayrizi and al-Khazin where each demonstrated particular cases of Menelaus' theorem that led to the sine rule,[7] or works composed as independent treatises such as:
- The "Treatise on the Figure of Secants" (Risala fi shakl al-qatta') by Thabit ibn Qurra.[6]
- Husam al-DIn al-Salar's Removing the Veil from the Mysteries of the Figure of Secants (Kashf al-qina' 'an asrar al-shakl al-qatta'), also known as "The Book on the Figure of Secants" (Kitab al-shakl al-qatta') or in Europe as The Treatise on the Complete Quadrilateral. The lost treatise was referred to by Al-Tusi and Nasir al-Din al-Tusi.[6]
- Work by al-Sijzi.[7]
- Tahdhib by Abu Nasr ibn Iraq.[7]
References
- ^ Follows Russel
- ^ Follows Hopkins, George Irving (1902). "Art. 983". Inductive Plane Geometry. D.C. Heath & Co..
- ^ Follows Russel with some simplification
- ^ See Michèle Audin, Géométrie, éditions BELIN, Paris 1998: indication for exercice 1.37, p. 273
- ^ Smith, D.E. (1958). History of Mathematics. II. Courier Dover Publications. p. 607. ISBN 0486204308.
- ^ a b c d Rashed, Roshdi (1996). Encyclopedia of the history of Arabic science. 2. London: Routledge. p. 483. ISBN 0415020638.
- ^ a b c Moussa, Ali (2011). "Mathematical Methods in Abū al-Wafāʾ's Almagest and the Qibla Determinations". Arabic Sciences and Philosophy (Cambridge University Press) 21 (1). doi:10.1017/S095742391000007X.
- Russell, John Wellesley (1905). "Ch. 1 §6 "Menelaus' Theorem"". Pure Geometry. Clarendon Press. http://books.google.com/books?id=r3ILAAAAYAAJ.
External links
- Alternate proof of Menelaus' theorem, from PlanetMath
- Menelaus From Ceva
- Ceva and Menelaus Meet on the Roads
- Menelaus and Ceva at MathPages
- Menelaus' Theorem by Jay Warendorff. The Wolfram Demonstrations Project.
- Weisstein, Eric W., "Menelaus' Theorem" from MathWorld.